Hello guy’s ! How are you?… I know you are also fine. Today we are going to learn discuss about Heat transfer.
The all engineering have lots of branches and here we will explain with you all detailed knowledge of mechanical engineering with the help of best notes.
Defintion of heat transfer
It is defined as the transmission of energy from one region to another due to temperature difference.
Types of Heat transfer:
There are three modes (ways) of heat transfer. They are;
1. Conduction .
2. Convection .
3. Radiation .
1. Conduction:
It is the process of heat transfer between two bodies or two parts of same body through molecules which are more or less stationery. E.g.
1) Fins provided on motor cycle engine.
2) Heating a metallic rod at one end and sense the heat at other end.
2. Convection:
It is the process of heat transfer from higher temperature to lower temperature due to movement of matter or fluid molectites (density differences).
E.g. heating of water.
Types of convection:
1. Free convection.
2. Forced convection.
1. Free convection:
The free convection occur where the fluid circulated by the virtue of the natural differences in densities of hot and cold fluids .
E.g. The heating of water in a container.
2. Forced convection:
The forced convection work is done by the blow or pump the fluid, it’s said to be forced convection. Or external force such as fans, blower, and pumps etc. giving rise to forced convection.
Ex: by providing the circulating fan in container.
3. Radiation :
It is process of a heat transfer between two body without any carrying medium through different kind of electro-magnetic wave. Radiation energy required no medium for transfer and will pass through vacuum .
E.g.
1) The sun heat from warming your face.
2) Heat from a light bulb .
3) Heat from a fire.
4) The heat from any thing else which is the warmer than it’s surrounding.
Fourier’s law of heat conduction :
For a homogeneous material the rate of heat transfer divide by area in any direction is linearly proportional to temperature gradient in the directions .
Mathematically ,
Q/A = dT / dx
Q/A = -K dT/dx
Q = -kA dT/dx
K is constant of proportionality is called as thermal conductivity . The negative sign indicates that there is decrease in temperature along the direction of heat flow.
Thermal conductivity :
It is defined as amount of energy conducted through a body of unit area and unit thickness in unit time when the difference in temperature between the faces carrying the heat flows 1°C .
lt is denoted by K.
Mathematically,
K= (Q/A) dx/dT.
W / mk.
Absorptivity :
It is defined as the ratio of amount of energy absorb to amount of energy incident on a body .
It is also called as coefficient of Absorptivity and it is denoted by a .
Mathematically, Absorptivity is expressed as
Absorptivity (a) = Qa / Qi
Where,
Qi is the amount of energy falling on a body.
Qa is the amount of energy absorbed by a body.
Reflectivity:
It is defines as the ratio of amount of energy reflected to amount of energy incident on a body .
It is also called as coefficient of reflectivity and it is denoted by Y.
Mathematically, Absorptivity is expressed as
Reflectivity (Y) = Qr / Qi.
Where,
Qi is the amount of energy falling on a body.
Qr is the amount of energy reflect the body.
Transmitivity :
It is defines as the ratio of amount of energy transmitted to amount of energy incident on a body .
It is also called as coefficient of transmitivity and it is denoted by town .
Mathematically, transmitivity is expressed as
Transmitivity = Qt / Qi
Where,
Qi is the amount of energy falling on a body .
Qt is the amount of energy transmitted by a body.
Black body:
A body which absorb all the incident radiation is called black body irrespective of its colour. For ; The black body condition is a = 1, Y=0, tow = 0.
Concept of black body :
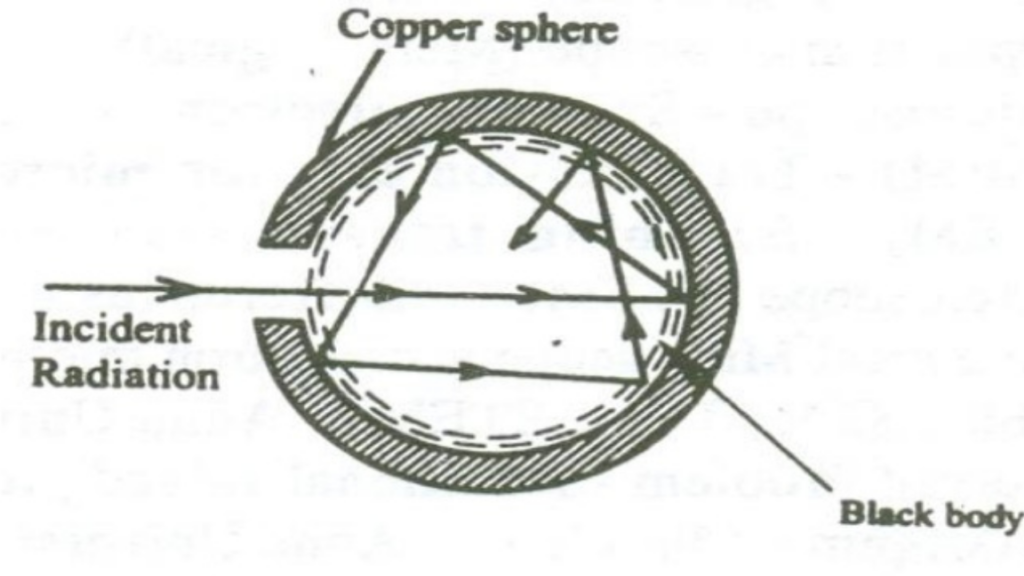
*A body which absorbs all the incident radiation is called as black body irrespective of its.
*Colour. For ; The black body condition is a = 0, Y = 0, tow = 0
*Actually no material available with a = 1.
To make practically a perfect body, a hollow sphere with small opening is used.
When ray enters the hollow body through an opening, a part of it is absorbed and part
is reflected inside.
*The reflected radiation will not find outlet and will again be incident on the inner surface Due to this sequence of reflection, almost complete incident radiation will be absorbed and none will come . Therefore, a small opening provided in a hollow sphere acts like a black body.
Grey body :
A body absorb a defined as the percentage of incident radiation irrespective of their wavelengths, the body is known as grey body. The body whose absorptivity do not vary with temperature and wavelength of the incident ray is called gray body.
Emissive power:
The emissive power is the total amount of thermal energy emitted area per unit time for all possible wavelengths .
Emissivity:
The emissivity of a body at a given temperature is the ratio of the total emissive power of a body to the total emissive power of a perfectly a black body at that temperatures.




Nice sir….?
?
?
Thank you?