Hello student’s How are you?.. I know you are fine. Today are going to study discuss about steam turbine.
Here, only you will get all detail knowledge your topic of mechanical engineering branch. Even, you will be get free study notes.
Steam turbine:
The steam turbine is a rotary heat engine that converted into thermal energy contained in
the steam into mechanical energy.
Classification of turbine :
1) According to working principles / Action of steam over moving blades :
a) Impulse turbine.
b) Reaction turbine.
c) Impulse-Reaction turbine.
2) According to the stages of expansion a of a steam turbine :–
a) Single stages turbine.
b) Multistage turbine.
3) According to the position of the shaft axis turbines:
a) The horizontal axis turbines.
b) The vertical axis turbines.
4) According to their nature of steam supply / Pressure of steam entering:
a) High pressure turbine.
b) Low pressure turbine.
5) According to the directions of a steam flow turbine:-
a) Axial flows turbine.
b) Radial flow turbine.
c) The tangential flows turbine.
d) Single flows or double flows .
(6) According to the exhaust a steam pressure turbine:
a) Condensing type of a steam turbine.
b) Non-condensing type steam turbine.
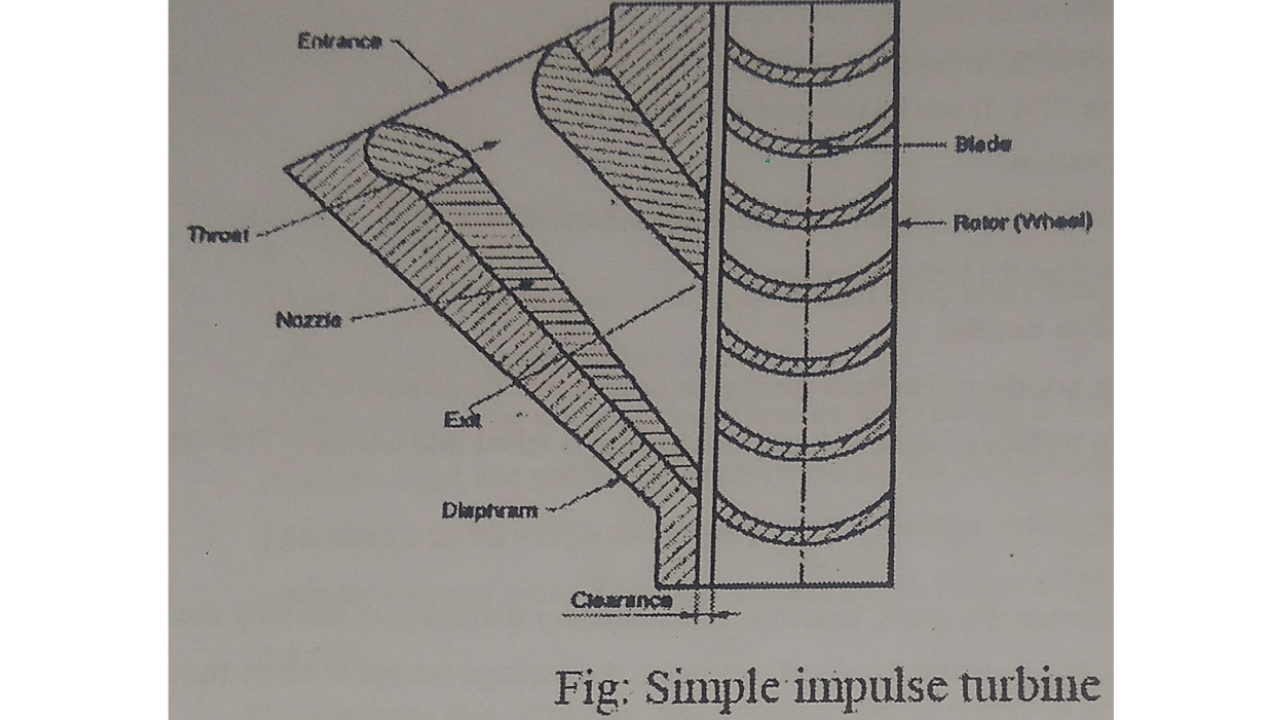
*Construction and working of Impulse Turbine:-
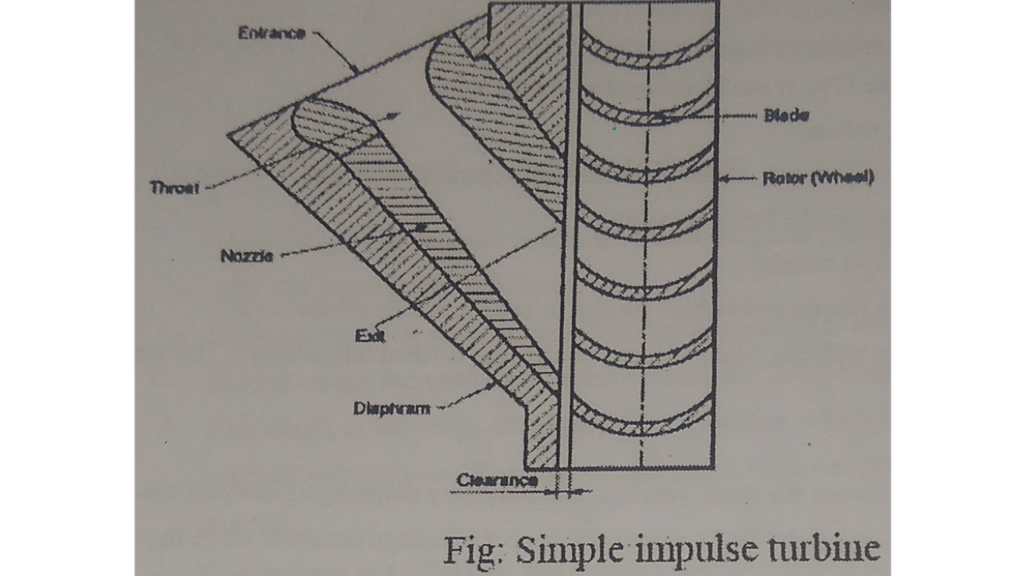
*The impulse turbine consists of a one set of the nozzle, which is followed by one set of moving blades as shown as in figure.
*In this types of turbine,the power is developed by the impulsive force.
*The high velocity steam jets are obtained by expansion of steam in the stationary nozzle. only.
*Steam passes through high velocity moving blade with drop pressure reduction in velocity.
*Thus in pure impulse turbine the high velocity jet having nozzle strikes on the blades mounted on the wheel attached to the shaft.
*These blades changes the direction of steam and momentum of the jet of steam, which rotates the shaft.
*The nozzle axis is angle inclined to the tangent of the rotor.
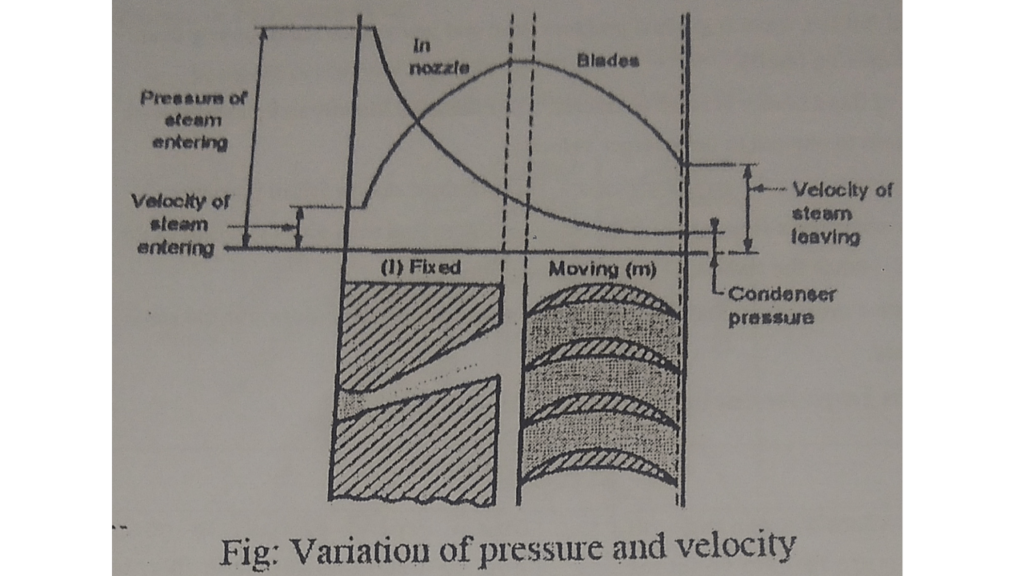
*construction and working of reaction turbine :
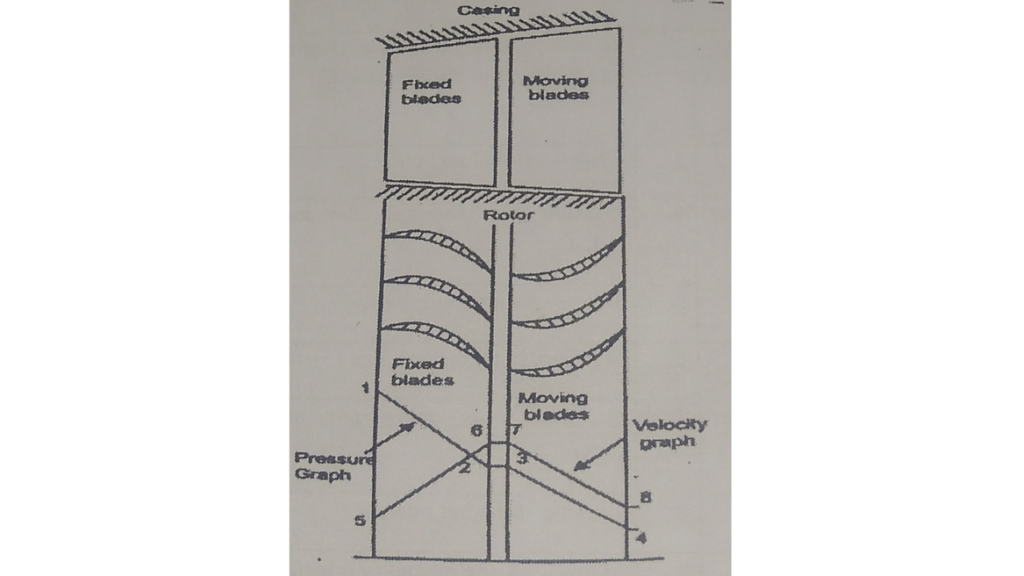
*In this type of turbine, there is a gradual pressure droped and take place continuously over the fixed and moving blades.
* The function of fixed blades is same as nozzle. They alter the direction of steam as well they allow steam to expand to have larger velocity.
*As the steam passes over the moving blades KE is obtained due fall in pressure.
*The steam expands the flowing over the moving blades and the gives reaction to the moving blades. the turbine is known as reaction turbine.
*Since the pressure drop is gradual, the number of stages required is more, for the same power developed.
Difference between Impulse turbine & Reaction turbine :–
*Impulse turbine :–
1.Steam completely expand nozzle & pressure remain constant flow passing through the blade.
2.Relative velocity increases as steam
passing over blades of impulse turbine is constant.
3.The blades is symmetrical profile.
4.Pressure is same at inlet and outlet
5.team velocity is very high.
6.The lesser no of stages required.
7.The occupies less space per unit power.
8.The suitable for a small power.
9.At low load the efficiency is low.
*Reaction turbine :
1.The steam expand the partially in nozzle & expansion take the rotor blade passage.
2. The relative velocity increases as steam passing over of the blade expands.
3.The blade is aerofoil section.
4.The pressure is a different at inlet and outlet
5.The steam velocity is not very high.
6.The more no of stages requires.
7.The occupies more space per unit power.
8.The suitable & higher power.
9.At low load, the efficiency is high.
*The energy losses in steam turbines:–
1.The residual velocity loss:
The steam turbine leaves with a certain absolute velocity which is results in loss of KE. This is loss is about the 10 to 12% It can be reduce by the multistaging.
2.The losses in regulating valves:
The throttling action in valves, the steam pressure droped occur. steam pressure entry to turbine is less boiler pressure.
3. The losses due friction in nozzle:
The friction occur both the nozzle & turbine blades. The nozzle efficiency is consider, where as in turbines, blade velocity coefficient is a taken into account. This loss is about 10%.
4.Loss due leakage –:
Shaft leakage occurs between bearings & stationary diaphragms carrying of nozzles of impulse turbines. In reaction turbine the leakage occurs at blade tips. this is about 1-2%
5.Loss due mechanical friction:
These occurs in bearing and may be reduce by lubrication.
6.Loss due wetness steam :-
Multistage turbine condensation dragging water particle. some K.E of steam is lost.
7.Radiation loss:
The turbines are heavily insulate to reduce the heat loss to surrounding by radiation these losses are negligible.
Thank you!!!
Kumar patil



?
Thank you?❤
❤️??
You not gonna believe this but Ive lost all day hunting for some articles about this. I desire I knew of this blog earlier, it absolutely was a brilliant read and in fact helped me out. Contain a ideal one!