Hello guy’s ! How are you?… I know you are also fine. Today we want to discuss different topics. I know you are an engineer, so the information that I am going to give you is about transformer part 1.
*Define transformer :-
Transformer is a static (or stationary) device in which electrical power in and circuit is transferred to another circuit with increase or decrease in voltage and current level but at constant in frequency.
*Working principle of transformer -:
The transformer operates the principle of mutual induction. Once ac supply is applied to primary it circulates by the ac flux in core which is that goes to link with secondary. The changing flux linking with secondary produces emf in secondary.
*Construction of transformer:-
Basically a transformer consists of 2 inductive coils and a laminated steel core. The coils are insulated from one another similarly as from w the steel core.
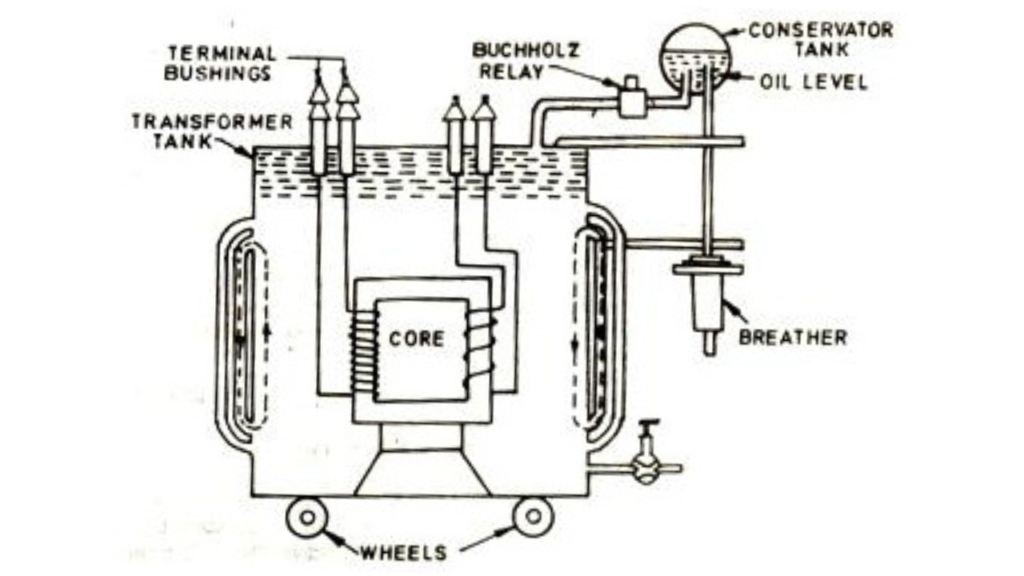
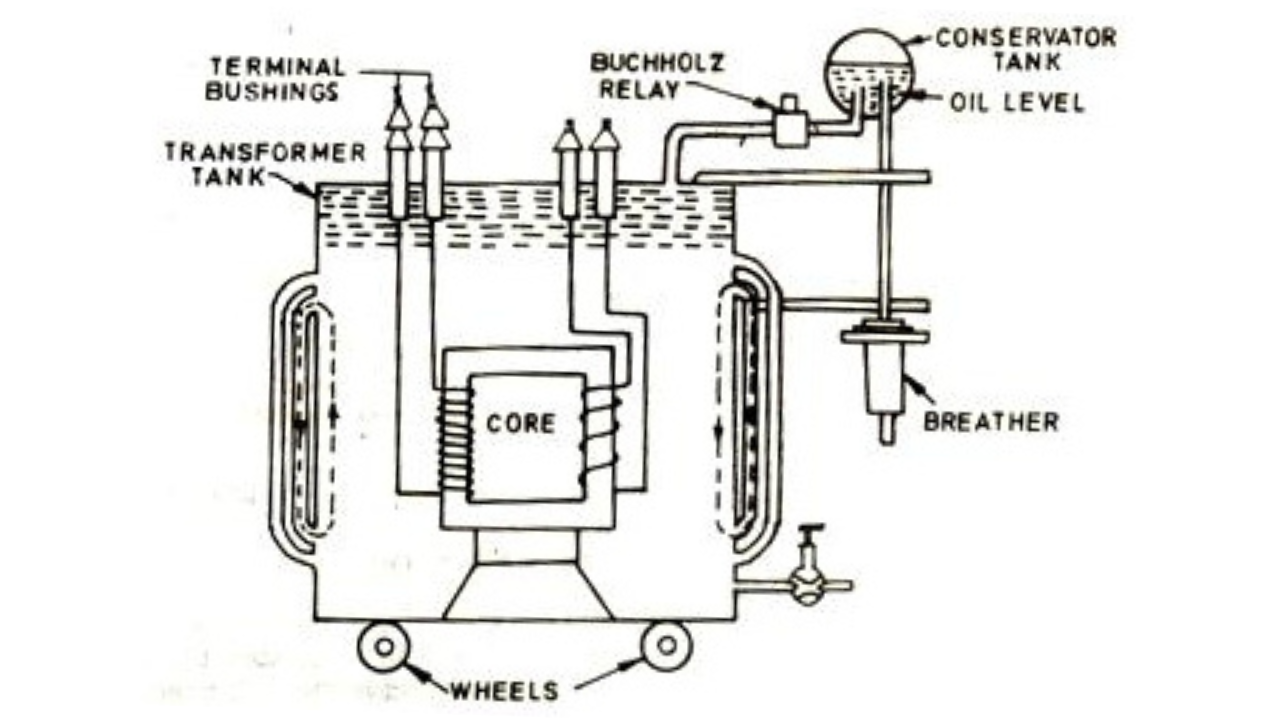
A might also consist of a container for winding and core assembly (called as tank), suitable bushings require taking out the terminals, oil conservator to produce oil within the tank for cooling purposes etc.
The as shown in figure at left illustrates the basic construction . The core is made by assembling (stacking) laminated sheets of steel, with minimum air -gap between them (to win continuous magnetic path).
The steel used has having high silicon content and sometimes heat treated, to produce high permeability and low hysteresis loss. Laminated sheets of steel are used for reduce the eddy current loss. The sheets are cut in the shape as an E,I and L. To avoid high reluctance at a joint, lamination are stacked by the alternating the sides of a joint. That is, if joint of initial sheet assembly are at front face, the joints of following assemble are kept at back face. The vertical portion of core is known as Limb or leg. The horizontal portion of the core is known as yoke.
*Working of transformer :-
1) When the primary coil is connected to AC provide, an AC current starts flowing through it.
2) The AC primary current produces an alternating flux within the core.
3) The changing flux links with both the primary and secondary coils and according to Faraday’s laws of a electromagnetic induction, emfs are induced with both the coils.
4) The emf is induced in a primary due to self-induction, whereas the emf is induced in a secondary due to mutual induction,
5) If the load is connected to secondary coil, the secondary emf delivers current through load and therefore the power is ultimately transferred from supply on primary side the load on secondary side without the electrical connection between primary coil and secondary coil.
6) The power is transferred through the magnetic coupling.
*Types Of Transformers :-
Transformers will be classified on completely different basis, like types of constructions, types of cooling etc.
(A) On the basis of a construction :-
Transformer will be classified into 2 types as ; (i) Core type and (ii) Shell type transformer, which are the described below.
(i) Core Type Transformer :-
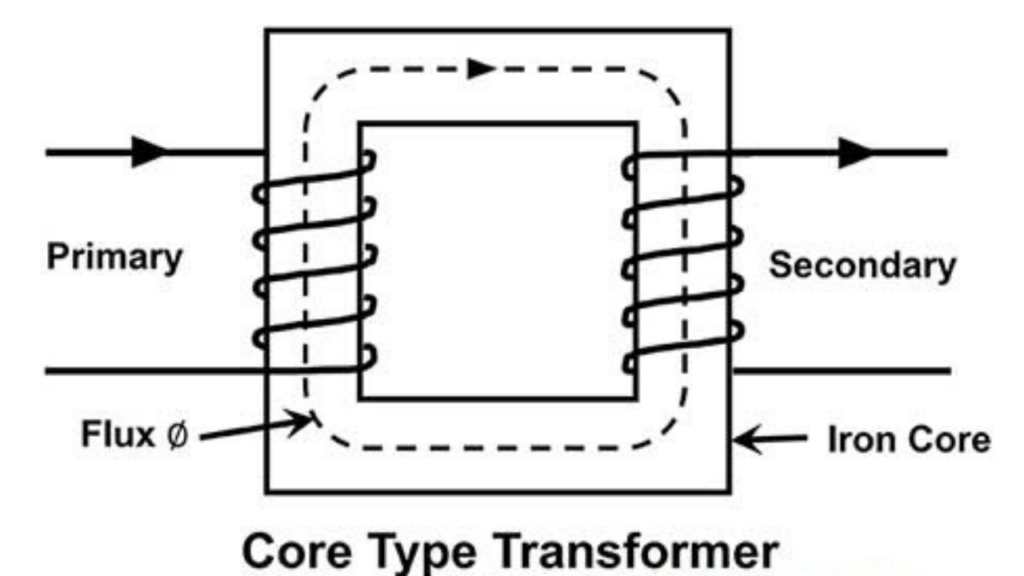
The core type transformer, coils are cylindrical former wound, mounted on the core limbs as shown within the figure above. The cylindrical coils have completely different layers and every layer is insulated from one another. Materials like paper, cloth or mica will be used for insulation. Low voltage coils are placed on nearer to the core, as they’re easier to insulate.
*Shell Type Transformer :-
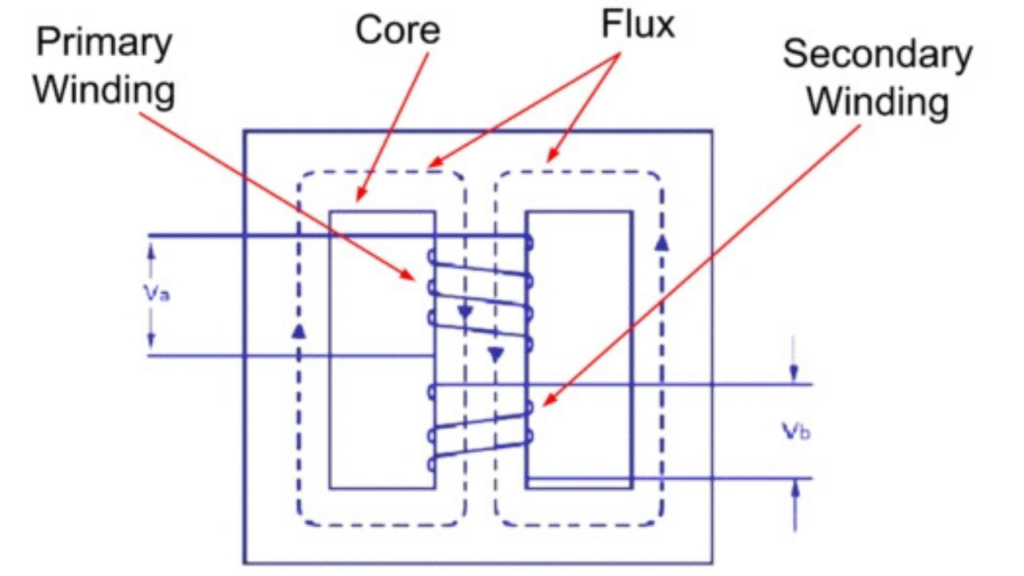
The winding are former wound and mounted in layers stacked with insulation between them. A shell type transformer might have simple rectangular form (as shown in the figure), or it might have a distributed form.
(B) On the basis of type of supply are :-
(1) Single phase transformer.
(2) Three phase transformer.
(c) On the basis of Application of transformer:-
- Power transformer -: Used in a high rating,transmission network.
- Distribution transformer -: Used in a distribution network , relatively lower rating than that of power transformers.
- Instrument transformer -: Used in a protection purpose and relay in different instruments in industries.
*Current transformer (CT).
*Potential transformer (PT).
(D) On the basis of Voltage :-
1) Step up transformer :- Voltage will increase (with a subsequent decrease in current) at secondary.
2) Step down transformer :- Voltage will decrease (with a subsequent increase in current) at secondary.



Brilliant
Thanks bhau?❤❤